AI in Healthcare: Transforming Efficiency and Patient Care
How AI can cut costs, improve care, and save lives in healthcare
Photo by Diana Polekhina on Unsplash
After eight years at UnitedHealth Group, I've witnessed firsthand the challenges and inefficiencies affecting the U.S. healthcare system: the potential for improvement is enormous, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers a compelling solution to address these inefficiencies.
The Current State of Healthcare Efficiency
Healthcare waste is a global issue, but the U. S. market has unique challenges. Consider the following statistics:
Administrative costs make up 34. 2% of total healthcare spending in the U. S. - twice as high as in Canada: that's about $2,497 per person every year [1].
Physicians spend nearly two hours on paperwork and admin tasks for every one hour of seeing patients [2].
These numbers show we urgently need more efficient systems in healthcare administration: this is where AI, Machine Learning (ML), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Data Science can play a crucial role.
AI-Driven Solutions for Healthcare Administration
1. Streamlining Complex Billing and Coding
Medical billing and coding is the backbone of getting paid in healthcare: it translates medical procedures, diagnoses, and equipment usage into standard codes.
These codes matter for a few reasons:
They make sure healthcare providers get paid correctly for their services
They let us document patient care in a standard way across different healthcare systems
They also help track public health trends and enable medical research
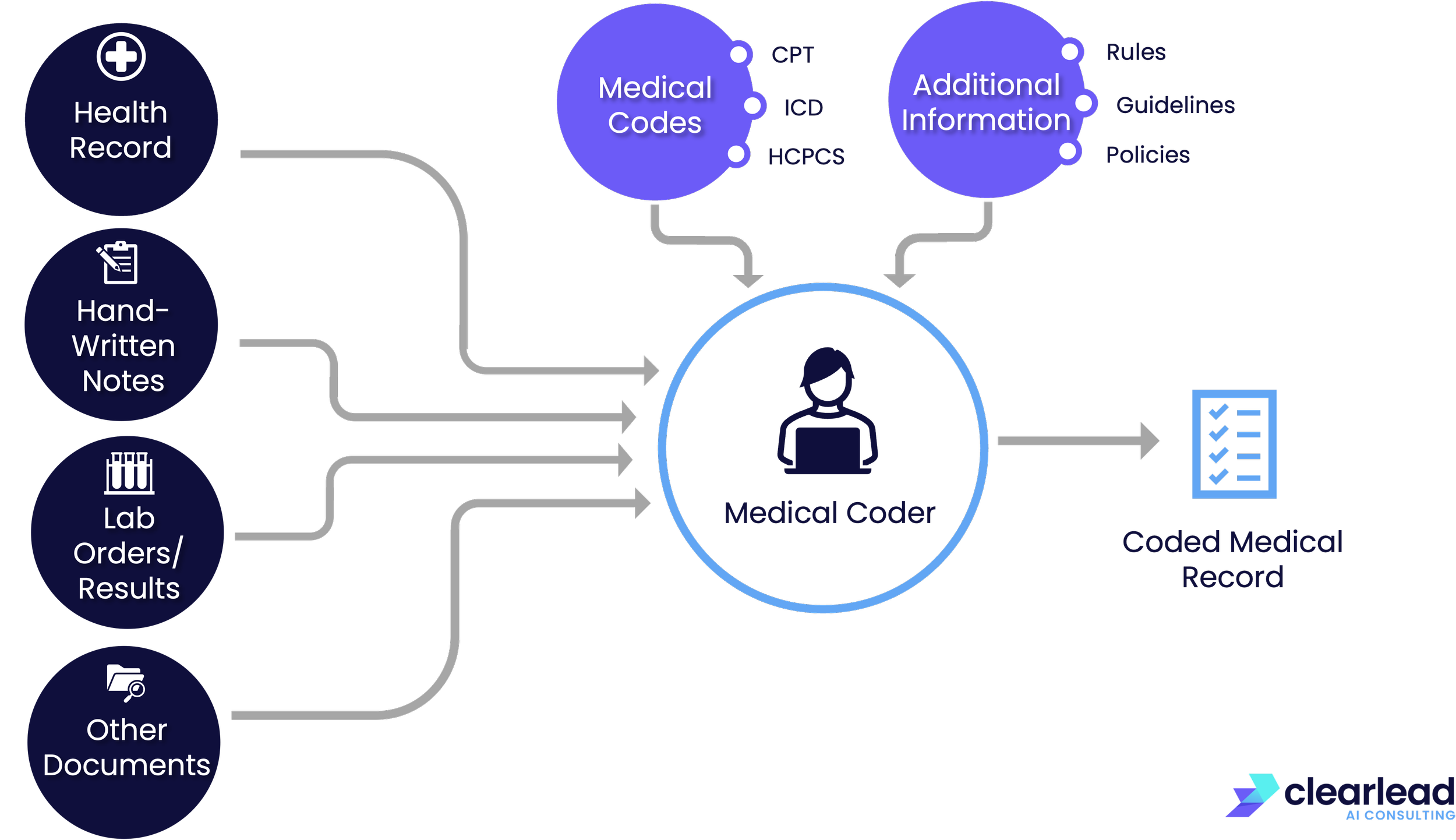
The following diagram illustrates the medical coding process:
The medical coding system, though essential, is extremely complex. It involves tens of thousands of codes, each with its own specific usage guidelines.
To complicate matters further, this system is not static: new codes are regularly introduced, and guidelines for existing codes can change.
This ever-evolving complexity creates numerous challenges, significantly impacting healthcare efficiency and costs.
However, AI solutions are in an ideal place to offer solutions to many of these challenges:
By automating coding and reducing errors AI can improve the billing and coding process, but also drive efficiencies in other areas:
Higher quality coding leads to better data for research, more accurate patient records and health trends overall.
Reducing errors speeds up the time for doctors to get reimbursed.
Reducing the admin burden frees up physicians to concentrate on patient care.
2. Addressing Fraud, Waste, Abuse, and Error (FWAE)
While fraud in healthcare is widely recognised as a major problem (since it usually gets the headlines), it is just one part of the broader Fraud, Waste, Abuse and Error (FWAE).
Fraud alone is estimated to cost the U.S. healthcare system between $100 billion and $300 billion annually [3].
But overall, the total impact of FWAE is much higher (with estimates of as much as $800 billion per year [4]).
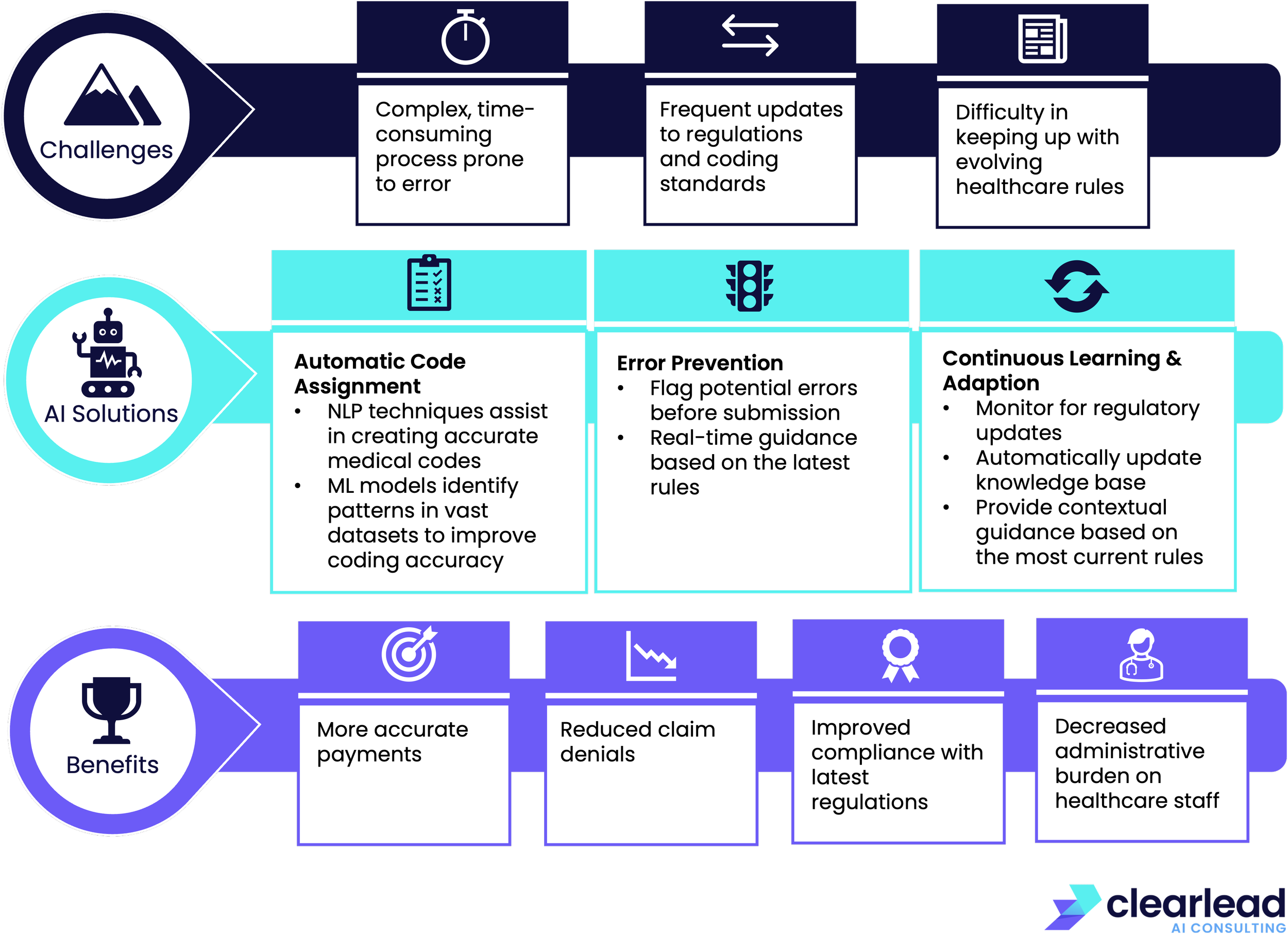
Here's an infographic summarising AI solutions for major challenges in healthcare related to financial waste, errors and abuse (FWAE):
Overall there are several positive benefits for healthcare organisations, to effectively applying AI to FWAE:
Reducing financial losses
Decreasing administrative burden
Speed up payments
Ensure regulatory compliance
But it's important to note that addressing FWAE is not simple, as we've already outlined, it is an extremely complex problem for many reasons.
However, there have been many recent advancements in AI (particularly in NLP and Data Science) that allow us to apply more advanced techniques to these problems.
From my own perspective, I've witnessed the success that these systems can achieve, especially when compared to traditional systems that are heavily reliant on human-coded rules: these AI solutions are much more effective and robust.
3. Solving EHR Interoperability
Another major issue within healthcare is fragmented patient records across incompatible EHR systems. This impedes care coordination and increases costs, as the following statistics show:
Lack of interoperability can affect patient care, resulting in “duplicate tests, medication errors, and gaps in care” [5]
Only 56% of hospitals can electronically find, send, receive, and integrate patient health information from outside sources [6].
AI offers some promising solutions:
Data Harmonisation: NLP can "translate" data between EHR formats
Unstructured Data Analysis: Extract key information from physician notes
Semantic Interoperability: Advanced NLP models can preserve meaning when sharing data
Automated Data Mapping: ML to streamline system integration
Secure Data Sharing: Techniques like federated learning enable privacy-preserving analytics
These improvements can lead to better coordination of care, fewer repeated tests, and more informed decision-making.
4. Boosting Operational Efficiency
AI can significantly improve healthcare operations, leading to better use of resources improved patient experiences, and cost savings.
Here are some key areas where it can make an impact:
Resource Allocation and Management
Predictive Analytics for Patient Flow - AI forecasts how many patients are coming, helping hospitals figure out staffing levels.
Managing Equipment and Supplies - AI makes sure hospitals have critical supplies but aren't overstocked.
Operating Room Scheduling - AI can optimise surgery schedules to maximise the use of expensive operating rooms and equipment
Enhancing Patient Experience
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants - Handle routine questions and appointment scheduling for patients.
Personalised Communication - Provided customised information to keep patients engaged.
Wait Time Reduction - Optimise patient flow to cut down waiting times.
Administrative Task Automation
Automated Data Entry - Scan clinical notes and enter key data into patient records automatically.
Claims Processing - Streamline and automatically identify errors and inconsistencies.
Clinical Decision Support
AI Diagnosis - Identify key patient info and provide access to relevant history and similar cases to assist diagnosis.
Treatment Plan Optimisation - Suggest personalised treatment plans based on patient data and current research.
Telehealth and Remote Monitoring
Smarter Telehealth Platforms - Effectively triage patients to decide if they need an in-person or online visit.
Remote Monitoring - Use data from wearables to allow providers to catch potential health issues early.
By implementing these solutions, healthcare groups can significantly improve efficiency. This allows the physicians to focus more on caring for patients. The end result: a more responsive and patient-focused healthcare system.
AI in Clinical Applications
While we've focused on business efficiency it's important to note the huge potential of AI in clinical applications:
Diagnostic Assistance: AI can review medical scans and patient history to help diagnose faster and more accurately.
Drug Discovery: ML models can speed up finding potential new medicines.
Custom Treatment Plans: AI can analyse patient data to make tailored treatment plans.
Predictive Analytics: AI can predict patient outcomes and flag high-risk individuals for preventative care.
One limiting factor to acknowledge here is that these applications typically require large amounts of high-quality medical data to train the underlying AI model, which can limit the real-world feasibility in some cases.
Challenges and Considerations
Implementing AI in healthcare isn't without challenges:
Data Privacy and Security: Protecting sensitive health information is vitally important.
System Integration: Integrating AI with existing healthcare IT systems can be complex.
Human Oversight: While AI can assist, human judgment is still crucial in healthcare.
Ethical Considerations: We must ensure that AI is used responsibly and fairly in healthcare.
The Future of AI in Healthcare
AI now has the chance to significantly enhance healthcare efficiency, profoundly changing how it is delivered and managed.
This potential includes:
Administrative tasks are streamlined, freeing healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care
FWAE is more effectively managed, potentially saving hundreds of billions in healthcare costs
Healthcare resources optimised for better patient outcomes through predictive analytics and smart allocation
More accurate and timely diagnoses, leading to improved patient care and potentially life-saving early interventions
Personalised treatment plans based on vast amounts of data, improving efficacy and reducing side effects
For healthcare providers, insurers, and policymakers, AI offers a real opportunity to build a more efficient, effective, and patient-centred healthcare system for everyone.
Are you ready to explore how AI can transform your healthcare organisation? Let's start a conversation about your journey towards a more efficient and effective future in healthcare, or you can check out our full set of AI consulting services.
References
[1] Woolhandler, S., Himmelstein, D. U., & Terry, K. (2022). Health Care Administrative Costs in the United States and Canada, 2017. Annals of Internal Medicine, 172(2), 134-142. https://doi.org/10.7326/M19-2818
[2] Sinsky, C., Colligan, L., Li, L., Prgomet, M., Reynolds, S., Goeders, L., Westbrook, J., Tutty, M., & Blike, G. (2016). Allocation of Physician Time in Ambulatory Practice: A Time and Motion Study in 4 Specialties. Annals of Internal Medicine, 165(11), 753-760. https://doi.org/10.7326/M16-0961
[3] National Health Care Anti-Fraud Association. (2023). The Challenge of Health Care Fraud. https://www.nhcaa.org/tools-insights/about-health-care-fraud/the-challenge-of-health-care-fraud/
[4] Managed Healthcare Executive. (2023). Fraud, Waste, and Abuse in Healthcare Claims and Who It’s Affecting: https://www.managedhealthcareexecutive.com/view/fraud-waste-and-abuse-in-healthcare-claims-and-who-it-s-affecting
[5] Adeniyi, A. O., Arowoogun, J. O., Chidi, R., Okolo, C. A., & Babawarun, O. (2024). The impact of electronic health records on patient care and outcomes: A comprehensive review. World Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews, 21(02), 1446-1455 DOI: https://doi.org/10.30574/wjarr.2024.21.2.0592
[6] Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology. (2020). State of Interoperability among U.S. Non-federal Acute Care Hospitals in 2018. https://www.healthit.gov/data/data-briefs/state-interoperability-among-us-non-federal-acute-care-hospitals-2018